Healthcare Real Estate Outlook Remains Strong in a Changing Environment
The U.S. medical office space market, including the Bay Area healthcare real estate sector, sustained steady growth in 2024. Vacancy rates declined, driven by strong demand consistently outpacing limited new supply. High construction and financing costs hindered significant development activity. However, MOB investment activity rebounded from the dip in 2023, signaling renewed confidence in the sector’s long-term performance.
As interest rates stabilized at a new baseline, investor sentiment grew stronger—especially as volatility in traditional office markets redirected capital toward more stable assets like medical offices. Looking ahead to 2025, the outlook remains cautiously optimistic. While investor appetite for medical office buildings (MOBs) is high, constrained inventory, rising material costs, and limited development pipelines continue to suppress supply.
Nevertheless, a growing aging population and evolving care models will continue fueling long-term demand for modern medical office space.
Aging Population
The ongoing aging of the Baby Boomer generation is a primary force behind escalating demand for healthcare services. This demographic shift is driving increased utilization across all types of medical office properties, with a particular need for accessible suburban medical office developments.
Advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The adoption of AI in healthcare real estate is expanding. Though still in early stages, AI technology is increasingly influencing both clinical and administrative functions. From diagnostics to back-end operations, AI is poised to play a pivotal role in reshaping healthcare delivery facilities, including Bay Area medical office spaces.
Integrated and Co-Located Healthcare Services
The trend of co-locating related services within the same or adjacent medical office properties is reshaping facility planning. Health systems are strategically aligning urgent care, imaging, and primary care centers to streamline operations and enhance the patient journey—especially in high-demand Bay Area MOB markets.
Inflation and Interest Rate Trends
Inflation remains above the Federal Reserve’s 2% benchmark despite sustained intervention. However, the consistency of interest rates over the past year is encouraging investor stability in healthcare real estate, bolstering capital flow toward medical office assets.
Lack of Affordable Housing for Healthcare Professionals
The nationwide housing shortage has a direct impact on the healthcare real estate sector. In high-cost areas like the Bay Area, elevated home and rental prices make it increasingly difficult for healthcare workers to reside near their places of employment—impacting staffing and operations.
Federal Spending and Policy Shifts
Federal cost-cutting measures may significantly affect the Department of Health and Human Services, with potential downstream effects on Medicare, Medicaid, and medical facility funding. These shifts create uncertainty for medical office construction and reimbursement planning.
Rising Construction Costs Impacting Development
The continued rise in material and labor costs, compounded by proposed tariffs, has stalled momentum for new MOB developments. Many healthcare developers are reassessing timelines, budgets, and procurement strategies in light of elevated pricing and supply chain disruptions.
Ongoing Healthcare Workforce Shortages
While healthcare employment has rebounded since 2021, a shortage remains—particularly in nursing and specialized physician fields. The lack of trained professionals is affecting provider expansion and new facility openings, especially in densely populated and service-scarce regions like the Bay Area.
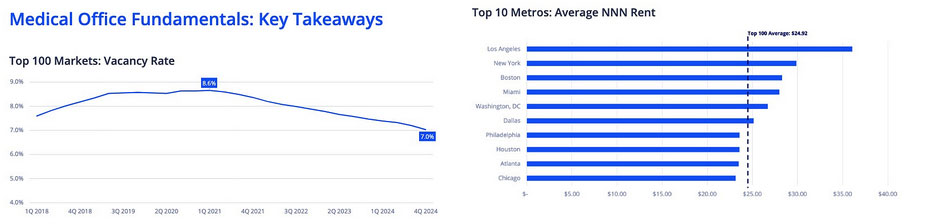
Medical Office Building (MOB) Vacancy, Rents, and Construction Performance
Vacancy Trends
In 2024, medical outpatient building (MOB) vacancies dropped to 7.0%, marking the 15th consecutive quarterly decline since Q1 2021. This underscores the high utilization and stable occupancy rates across U.S. and Bay Area MOB markets.
Rental Rates
Average triple-net (NNN) asking rents for MOBs rose to $24.92/SF in 2024—an annual increase of 2.7%. Ongoing supply limitations continue to exert upward pressure on lease rates in prime healthcare real estate markets.
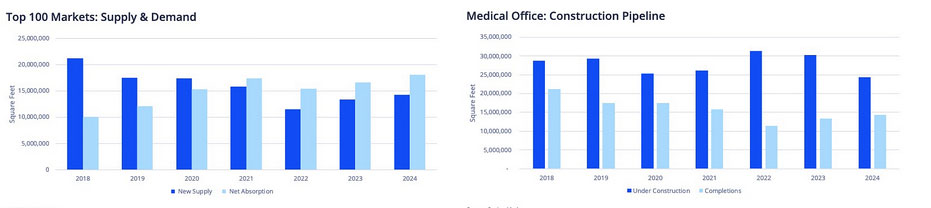
Absorption and Demand
With 18.0 million square feet (MSF) absorbed in 2024—up 10% from 2023—MOB demand outpaced supply for the fourth consecutive year. Despite 14.3 MSF of new completions, the sector’s absorption rate highlights sustained user demand.
Construction Pipeline
While new space deliveries increased again in 2024, reaching 14.3 MSF, higher borrowing costs and material pricing led to decreased construction starts. Only 8.3 MSF broke ground in 2024—down from 12.2 MSF in 2023—marking the lowest level in eight years.
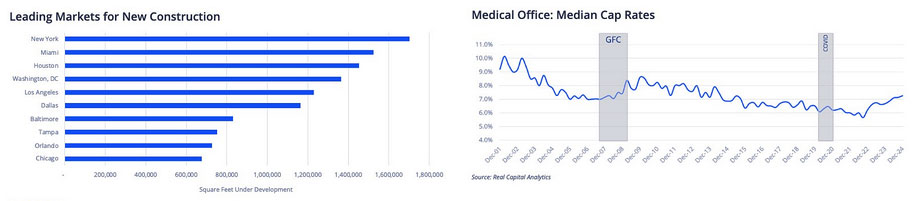
Top Markets for New MOB Development
Construction Hotspots
New York led all U.S. markets with 1.7 MSF of MOB construction underway at year-end 2024—representing 7% of development across the Top 100 markets. Overall, the Top 10 markets account for nearly half of all new medical office construction activity nationwide.
Cap Rate Trends
Median MOB cap rates climbed 60 basis points over the year to 7.3%—the highest level recorded since Q2 2014—highlighting the shifting return expectations for investors in healthcare real estate assets.
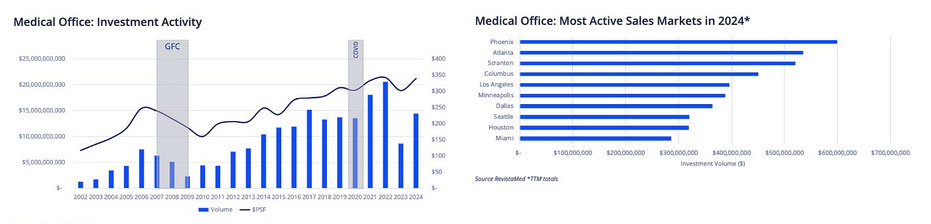
MOB Investment Volume and Pricing Trends
Investment Performance
In 2024, MOB investment activity totaled $14.4 billion—up 67.3% year-over-year. Although this fell short of 2022’s peak of $20.5 billion, the average sales price climbed from $302/SF in 2023 to $339/SF in 2024, exceeding the 10-year average of $300/SF.
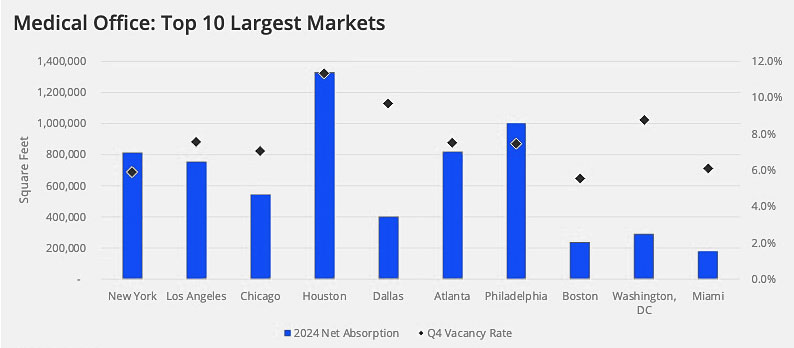
Leading U.S. MOB Markets: Development and Rent Growth
The Top 10 U.S. medical office markets built 4.4 MSF of new space in 2024—representing 40% of development in the Top 50 markets. These markets also absorbed 6.3 MSF of MOB space, with Houston and Philadelphia leading the pack. Houston completed 970,000 SF, while Philadelphia added 752,000 SF. Boston, by contrast, recorded the lowest new supply with just 91,000 SF.
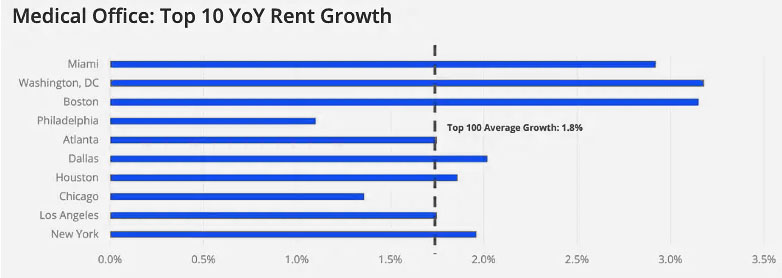
Rent Growth in Key Markets
Eight of the Top 10 markets reported rent increases above the national average of 1.8% YOY, highlighting broad-based growth and resilience in leading MOB leasing markets—with Chicago and Philadelphia posting modestly lower increases.
Healthcare Industry Outlook for 2025
Hospital systems and healthcare providers will encounter many challenges and difficult decisions, including tighter margins and labor constraints. Technological advancements, including the integration of AI on a larger scale, can help streamline operations while advancing medical analysis. Investment and merger activity is expected to heat up as interest rates hold steady, and buyers are poised to invest more in healthcare properties. New federal policies’ effect on construction material prices will impact health systems’ ability to build new facilities.
Challenges
The healthcare industry has added almost 2.0 million jobs since the fall of 2021, surpassing the loss of 1.6 million jobs due to the COVID-19 pandemic during March and April of 2020. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that the registered nurse (RN) workforce is expected to grow 6% over the next decade. However, the retirement-eligible population is rising, adding pressure to backfill those positions as demand for medical services from the Baby Boomer generation increases. The American Association of Colleges of Nursing reported a drop in enrollment for PhD and master’s nursing programs in 2023. U.S. nursing schools turned away more than 65,000 qualified applications due to a lack of faculty, clinical sites, classrooms, and clinical preceptors. As a result, the Health Resources and Services Administration projects a shortfall of 63,000 RNs by 2030.
At the same time, the Association of American Medical Colleges is projecting a physician shortage of 86,000 by 2036. Almost one-fifth of the physician workforce is approaching retirement age, while population growth and aging continue to drive the need for more doctors. The total number of medical school applicants dropped 1.2% in the 2024–2025 school year to the lowest level since 2017–2018.
The shortage of eligible RNs and physicians puts upward pressure on compensation, and overall labor costs continue to rise. Low unemployment rates make attracting and retaining qualified healthcare professionals challenging. This can make expanding service offerings or opening new locations much more difficult.
Another challenge is the rising cost of construction materials. The scarcity of materials has been driving up prices for several years, and potential tariffs announced in early 2025 on aluminum, steel, and lumber will impede development in the short term. Many developers and health systems are looking to stockpile materials to avoid higher costs.
The federal government’s proposed budget cuts are projected to significantly impact the Department of Health and Human Services, but the actual impact is unclear. Proposed cuts to scientific research may also affect potential breakthroughs, funding for research grants, and support of Medicare/Medicaid. While many of these proposed cuts are being challenged in the courts, health systems are paying close attention and evaluating the impacts if cuts are ultimately enacted.
Opportunities
The aging population is placing increased demands on the healthcare industry across a broad range of specialties. This creates opportunities for health systems to expand offerings or look for acquisition targets to add to their capabilities. The shifting demographics also create new geographic opportunities, as many Baby Boomers gravitate towards 55-plus communities further from city centers. Providers are finding opportunities to open new locations closer to these communities.
The ability to co-locate services is expanding as providers look to maximize the patient experience and streamline operations and services. Putting similar services in the same setting can improve space and time usage. Placing related services (i.e., primary care, imaging, and urgent care) next door to one another can save time in diagnosis and treatment while also helping strengthen patient loyalty and retention.
While the medical use of AI is still in its early stages, its potential is promising. It can streamline administrative tasks such as scheduling and billing, power telemedicine platforms for underserved rural areas, help detect abnormalities in medical imaging, and develop personalized treatment plans.
Moreover, AI’s predictive analytics can assist healthcare resource planning and allocation, enhancing care delivery.
Investment volume is expected to rise in 2025 as confidence in the stability of both interest and Treasury rates increases. The healthcare market offers attractive risk/return investment opportunities driven by a growing population, aging demographics, and underserved regions. In contrast to the broader issues affecting traditional office buildings, medical properties remain resilient as demand consistently outstrips supply.
Conclusion
Demand for healthcare real estate is expected to increase in 2025, continuing post-COVID trends. Health systems are integrating technology, including AI, on a larger scale to serve patients while updating their infrastructure to be more efficient. Although development may be limited by the high costs of capital, materials, and labor, demand is driving new construction in many parts of the U.S. Finding creative solutions to staffing shortages will be a vital part of keeping high-quality medical care available while enhancing care delivery with a positive patient experience.












